- What percent has their price increased since it first opened? (percent increase)
- What percent has the price increased annually on average? (compound interest)
- How has Motel 6 increased their prices compared to inflation?
- What is a guess that is too low for the percent increase?
- What is a guess that is too high for the percent increase?
- What is your best guess for the percent increase?
- What information do we need to know?
The second and third challenges look at the problem from a historical perspective. Using the generic compound interest formula and assuming:
- we are going from 1962 to 2013 for a total of 51 years
- interest is only compounded once a year
we get:
65.99 = 6(1 + r)^51
which ultimately gives us an average annual price increase percentage of approximately 4.81%.
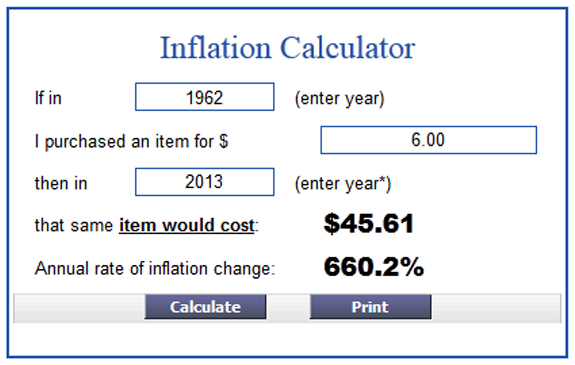
The final challenge is an extension and involves comparing Motel 6’s average annual price increase percentage to the United States average annual inflation rate over the same period. According to a US Inflation Calculator, if Motel 6 had only adjusted its prices to keep up with inflation, the price should be $45.61. So, students will have to determine what interest rate would have resulted in that price. That gives us:
45.61 = 6(1 + r)^51
which ultimately gives us an average annual inflation percentage of approximately 4.05%.
It is worth encouraging students to reflect on how an interest rate difference of only 0.76% has resulted in significantly different prices when compounded annually over 51 years.
- Current price at a Motel 6

- Original price at a Motel 6 in 1962

- Average annual inflation in the United States from 1962 to 2013
- CCSS 7.RP.3 Use proportional relationships to solve multistep ratio and percent problems. Examples: simple interest, tax, markups and markdowns, gratuities and commissions, fees, percent increase and decrease, percent error.
- CCSS A-SSE.1b Interpret complicated expressions by viewing one or more of their parts as a single entity. For example, interpret P(1+r)n as the product of P and a factor not depending on P.
- CCSS F-BF.1 Write a function that describes a relationship between two quantities.
- CCSS F-IF.8b Use the properties of exponents to interpret expressions for exponential functions. For example, identify percent rate of change in functions such as y = (1.02)t, y = (0.97)t, y = (1.01)12t, y = (1.2)t/10, and classify them as representing exponential growth or decay.
- CCSS F-LE.1 Distinguish between situations that can be modeled with linear functions and with exponential functions.



Just like gas went from 22cents to $4 and a McDonalds hamburger went from 15 cents to several dollars.